Table of Contents
- Introduction to Demand Generation
- Understanding the Demand Generation Framework
- Building Your Demand Generation Strategy
- Core Demand Generation Channels and Tactics
- Content Marketing for Demand Generation
- Account-Based Marketing (ABM) Integration
- Technology Stack and Tools
- Measuring Demand Generation Success
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Future Trends in B2B Demand Generation
1. Introduction to Demand Generation
Demand generation represents the systematic approach to creating awareness, interest, and engagement for your B2B or SaaS solution across the entire buyer journey. Unlike lead generation, which focuses solely on capturing contact information, demand generation encompasses a broader philosophy of building genuine market interest and nurturing prospects through education and value delivery.
For B2B and SaaS companies targeting North American markets, demand generation has evolved from a marketing buzzword into a critical revenue driver. The modern buyer completes 60-70% of their purchasing journey before ever engaging with sales, making strategic demand generation essential for market leadership.
What Demand Generation Actually Means
Demand generation orchestrates the full spectrum of marketing activities that create awareness and enthusiasm for your products or services. This includes everything from brand awareness campaigns to bottom-of-funnel conversion tactics, unified under a cohesive strategy designed to move prospects toward purchase decisions.
The fundamental distinction lies in intent: while lead generation extracts value from existing demand, demand generation creates and nurtures that demand from inception. This approach builds sustainable growth rather than depleting finite market awareness.
Why Traditional Marketing Falls Short
Traditional marketing approaches often fragment the buyer journey into disconnected campaigns and channels. Sales receives leads without context, marketing measures vanity metrics without revenue connection, and prospects experience disjointed messaging across touchpoints.
Demand generation solves this by creating an integrated system where each marketing activity contributes to a unified goal: moving ideal customer profiles through awareness, consideration, and decision stages with relevant, timely engagement.
2. Understanding the Demand Generation Framework
The Demand Generation Funnel
The demand generation funnel differs from traditional marketing funnels by emphasizing education and value creation at every stage:
Top of Funnel (TOFU) – Awareness Stage: At this stage, your ideal customers recognize they have a problem but may not understand the full scope or available solutions. Your demand generation efforts focus on educational content that illuminates problems, explores industry trends, and positions your company as a thought leader.
Key activities include publishing research reports, hosting educational webinars, creating comprehensive guides, and establishing presence in industry conversations. The goal centers on building brand awareness and establishing credibility rather than pushing product features.
Middle of Funnel (MOFU) – Consideration Stage: Prospects now actively evaluate potential solutions and compare different approaches. They consume detailed comparison content, case studies, product demonstrations, and analytical frameworks that help them assess options.
Your demand generation strategy here emphasizes demonstrating unique value propositions, showcasing customer success stories, and providing tools that facilitate evaluation. This stage requires balancing educational content with strategic positioning that highlights your competitive advantages.
Bottom of Funnel (BOFU) – Decision Stage: Buyers narrow their options and prepare for purchase decisions. They seek validation through customer testimonials, detailed pricing information, ROI calculators, and proof of concept opportunities.
Demand generation at this stage removes friction from the buying process, addresses final objections, and facilitates smooth handoffs to sales teams. Content becomes highly specific, addressing implementation concerns and demonstrating proven results.
The Buyer Journey in B2B and SaaS
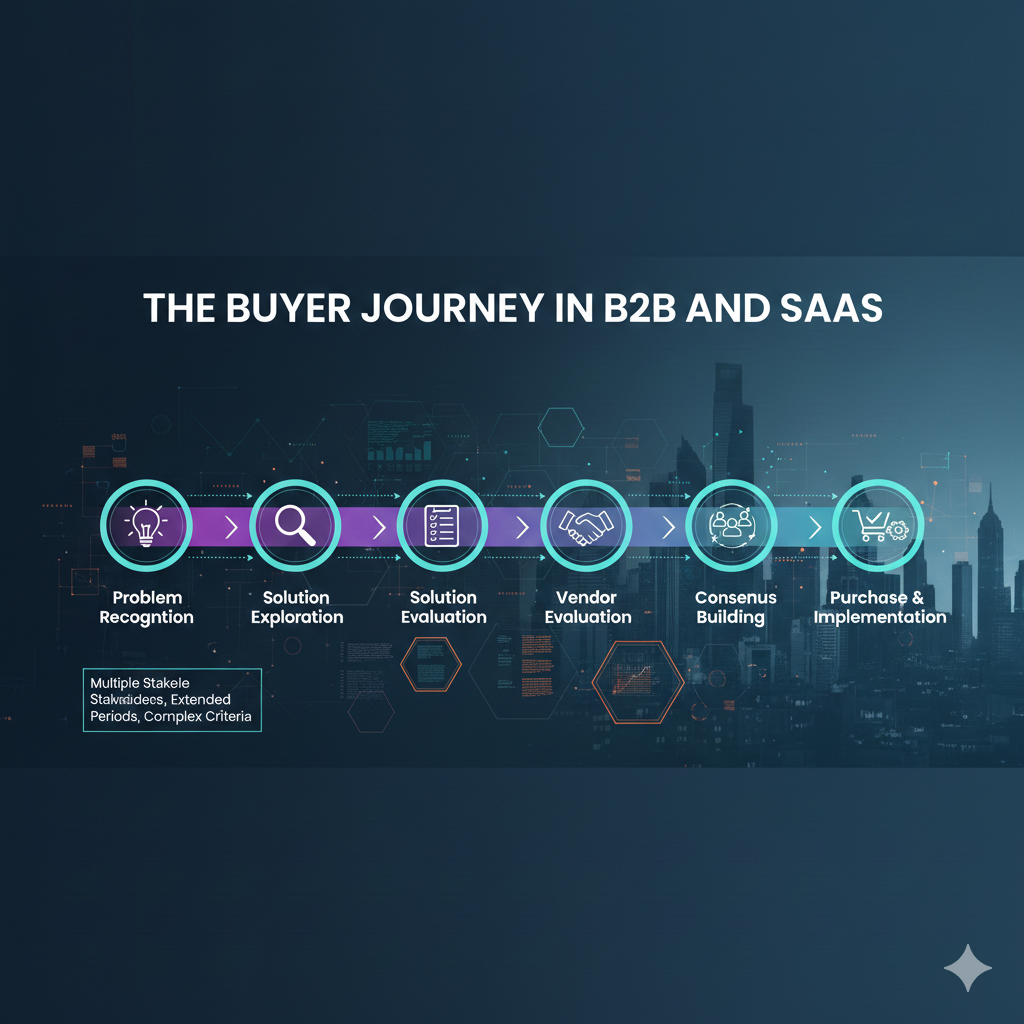
B2B buying processes involve multiple stakeholders, extended evaluation periods, and complex decision criteria. A typical B2B buyer journey spans several months and includes:
Problem Recognition: Stakeholders identify operational challenges or growth opportunities that require new solutions. This recognition often emerges from performance gaps, competitive pressure, or strategic initiatives.
Solution Exploration: Buying committees research available approaches, consulting peer networks, reviewing analyst reports, and consuming educational content. They build internal business cases and establish evaluation criteria.
Vendor Evaluation: Organizations shortlist potential providers, requesting demonstrations, proposals, and references. Technical evaluations, security reviews, and commercial discussions occur simultaneously.
Consensus Building: Stakeholders align on preferred solutions, securing necessary approvals and addressing concerns from legal, finance, security, and operational teams.
Purchase and Implementation: Final contracts are negotiated, leading to onboarding and deployment. The experience during this phase significantly impacts long-term customer success.
Demand Generation vs Lead Generation
These terms are often confused, but understanding their distinction proves crucial for strategic success:
Demand Generation creates market awareness and builds interest in your solution category. It educates prospects, establishes thought leadership, and nurtures relationships over time. Success metrics include market awareness, content engagement, pipeline influence, and revenue impact.
Lead Generation captures contact information from prospects demonstrating purchase intent. It focuses on conversion optimization, form completions, and marketing qualified lead volume. Lead generation often relies on gated content and direct response tactics.
The most effective strategies integrate both approaches, using demand generation to build market presence and lead generation to capture and convert active buyers. The ratio depends on market maturity, competitive dynamics, and growth objectives.
3. Building Your Demand Generation Strategy
Defining Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
Your ICP represents the perfect fit customer who receives maximum value from your solution and generates optimal revenue for your business. Developing precise ICPs requires analyzing:
Firmographic Characteristics: Company size, industry vertical, revenue range, geographic location, growth stage, and technology adoption patterns. B2B and SaaS companies often segment by employee count, annual revenue, and market segment.
Behavioral Indicators: Technology stack usage, buyer journey patterns, content consumption preferences, channel engagement, and decision-making processes. Understanding how your best customers behave guides channel and content strategies.
Pain Points and Priorities: Specific challenges your solution addresses, business objectives driving purchase decisions, and competitive alternatives being considered. Deep understanding of motivations enables resonant messaging.
Buying Committee Structure: Key stakeholders involved in decisions, influence patterns within organizations, approval processes, and timeline expectations. B2B purchases typically involve 6-10 decision influencers.
Refining your ICP should be an ongoing process informed by customer data, win/loss analysis, and market feedback. The most successful demand generation programs focus resources on the highest-value segments rather than attempting to serve everyone.
Creating Buyer Personas
While ICPs define target companies, buyer personas characterize individual decision makers and influencers within those organizations. Effective personas include:
Role and Responsibilities: Job titles, organizational position, primary objectives, performance metrics, and daily challenges. Understanding what drives individual success enables personalized messaging.
Information Needs: Preferred content types, consumption patterns, trusted information sources, and research behaviors. Different personas require different content approaches.
Objections and Concerns: Common barriers to purchase, risk factors, competitive comparisons, and validation requirements. Addressing these proactively builds confidence.
Influence and Authority: Decision-making power, budget control, and ability to champion solutions internally. Mapping influence patterns optimizes stakeholder engagement.
Develop 3-5 detailed personas representing your primary buying committee members. Include direct quotes from customer interviews, specific challenges they face, and content preferences based on actual behavior data.
Setting SMART Goals and KPIs
Effective demand generation requires clear, measurable objectives aligned with revenue targets:
Awareness Metrics: Brand search volume, website traffic from target accounts, social media reach, content consumption rates, and market share of voice. These indicate market presence and mindshare.
Engagement Metrics: Content downloads, webinar attendance, email engagement rates, time on site, pages per session, and return visitor rates. Engagement signals growing interest and relationship development.
Pipeline Metrics: Marketing qualified leads (MQLs), sales accepted leads (SALs), opportunity creation, pipeline value influenced, and pipeline velocity. These connect marketing activities to revenue outcomes.
Revenue Metrics: Customer acquisition cost (CAC), marketing-sourced revenue, influenced revenue, customer lifetime value (LTV), and return on marketing investment. Ultimate success measures tie to business growth.
Establish baseline measurements, set quarterly improvement targets, and create dashboards that provide real-time visibility into performance. Goals should stretch capabilities while remaining achievable with focused execution.
Budget Allocation
Strategic budget allocation balances experimentation with proven tactics:
Channel Distribution: Allocate resources across content marketing, paid advertising, events, technology tools, and team capabilities. Most B2B companies dedicate 40-50% to content creation and distribution, 25-30% to paid channels, and 20-25% to technology and operations.
Funnel Stage Investment: TOFU activities typically require 40-45% of budget to build awareness, MOFU engagement demands 30-35%, and BOFU conversion tactics need 20-25%. Adjust based on market position and growth stage.
Testing Allocation: Reserve 10-15% of budget for experimenting with new channels, tactics, and creative approaches. Innovation prevents stagnation and uncovers competitive advantages.
Fixed vs Variable Costs: Balance long-term investments in team, technology, and foundational content with flexible spending on campaigns and paid channels. This enables agility while maintaining consistency.
Review allocation quarterly based on performance data, adjusting investments toward highest-performing channels while maintaining diversification to reduce risk.
4. Core Demand Generation Channels and Tactics
Content Marketing
Content marketing forms the foundation of effective demand generation, providing value that attracts, educates, and converts ideal customers:
Educational Blog Content: Publish consistent, high-quality articles addressing buyer questions, challenges, and interests at every funnel stage. Focus on search optimization, readability, and actionable insights. Aim for 2-4 substantive posts weekly covering industry trends, how-to guides, and thought leadership.
Long-Form Pillar Content: Create comprehensive guides serving as authoritative resources on key topics. These assets drive organic traffic, establish expertise, and support lead generation. Update annually to maintain relevance and search rankings.
Video Content: Develop explainer videos, customer testimonials, product demonstrations, and educational series. Video drives higher engagement than text alone and supports multiple distribution channels.
Podcasts and Audio Content: Launch interview series with industry experts, customer success stories, or educational programming. Audio content builds relationships and reaches prospects during commutes and downtime.
Original Research and Data: Conduct surveys, analyze industry trends, and publish unique findings. Original research generates media coverage, backlinks, and differentiation while providing valuable assets for demand generation campaigns.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Organic search drives sustainable, high-quality traffic that converts efficiently:
Technical SEO Foundation: Ensure fast page loading, mobile responsiveness, clean site architecture, secure connections, and crawlability. Technical excellence prevents visibility limitations and improves user experience.
Keyword Strategy: Research and target terms your ideal customers use when seeking solutions. Balance high-volume competitive terms with specific long-tail phrases indicating purchase intent. Create content hubs around core topics.
On-Page Optimization: Optimize title tags, meta descriptions, headers, and body content for target keywords while maintaining natural readability. Include internal linking that guides visitors through related content.
Link Building: Earn backlinks from authoritative industry sites through guest contributions, partnerships, digital PR, and creating linkable assets. Quality backlinks significantly impact rankings and referral traffic.
Local SEO: For companies with geographic focus, optimize for local search through Google Business Profile, location pages, and local citations. This proves especially valuable for professional services and regional SaaS providers.
Paid Advertising
Paid channels accelerate demand generation and enable precise targeting:
Search Engine Marketing (SEM): Bid on high-intent keywords to capture active buyers. Focus on bottom-funnel terms initially, expanding to educational queries as campaigns mature. Maintain tight keyword grouping and compelling ad copy.
LinkedIn Advertising: Leverage LinkedIn’s professional targeting for reaching decision makers by job title, company, industry, and skills. Effective formats include sponsored content, message ads, and dynamic ads. LinkedIn typically delivers higher quality leads despite higher costs.
Display and Retargeting: Build awareness through display advertising on industry sites and retarget website visitors with relevant messaging. Use audience segmentation to serve personalized content based on funnel stage and behavior.
Content Syndication: Distribute content through networks that place it on relevant publisher sites, capturing leads from engaged readers. Effective for reaching new audiences and generating MQLs at scale.
Social Media Advertising: Beyond LinkedIn, consider Facebook and Instagram for reaching specific personas, Twitter for industry conversations, and emerging platforms where your audience congregates.
Email Marketing
Email remains one of the highest-ROI channels for demand generation:
Welcome Series: Onboard new subscribers with curated content introducing your brand, solutions, and value proposition. First impressions significantly impact long-term engagement.
Nurture Campaigns: Develop multi-touch sequences that educate prospects based on their interests, behavior, and funnel stage. Personalization and relevance determine success. Include educational content, case studies, and thought leadership.
Newsletter Programs: Maintain regular communication with subscribers through curated industry insights, company updates, and valuable resources. Consistency builds mindshare and relationship strength.
Event Promotion: Drive registration for webinars, workshops, and conferences through targeted email campaigns. Follow up with attendees and no-shows with relevant content and conversion opportunities.
Re-engagement Campaigns: Win back inactive subscribers through strategic messaging highlighting new offerings, content, or value propositions. Clean your list regularly to maintain deliverability.
Webinars and Virtual Events
Interactive experiences build relationships and demonstrate expertise:
Educational Webinars: Host expert presentations on industry challenges, best practices, and emerging trends. Focus on education over promotion, delivering genuine value that builds trust.
Product Demonstrations: Showcase solution capabilities and use cases through live demonstrations. Interactive formats allow prospects to ask questions and see real-world applications.
Panel Discussions: Convene industry experts, customers, and thought leaders for multi-perspective conversations. Panels provide diverse viewpoints while associating your brand with industry leaders.
Workshop Series: Develop hands-on training programs that help prospects develop skills or implement strategies. Workshops position you as invested in customer success beyond selling.
Virtual Conferences: For companies with substantial reach, host multi-session events featuring keynotes, breakouts, and networking. Virtual conferences generate significant awareness and engagement.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
ABM focuses resources on high-value target accounts through personalized engagement:
Target Account Selection: Identify accounts representing ideal customers with significant revenue potential. Consider fit, opportunity size, competitive positioning, and relationship status. Quality matters more than quantity.
Account Research: Develop deep understanding of target accounts including business priorities, challenges, recent developments, stakeholder mapping, and competitive landscape. Intelligence enables personalization.
Personalized Campaigns: Create account-specific content, messaging, and experiences. This might include custom landing pages, personalized videos, direct mail, targeted advertising, and coordinated outreach.
Multi-Channel Orchestration: Engage accounts through coordinated touchpoints across multiple channels, creating consistent presence and message reinforcement. Surround accounts with relevant content.
Sales Alignment: ABM requires tight coordination between marketing and sales teams. Shared goals, regular communication, and collaborative planning ensure consistent execution.
Social Media and Community Building
Strategic social presence builds brand awareness and relationship:
LinkedIn Strategy: Publish thought leadership content, engage in industry conversations, and build executive visibility. LinkedIn serves as the primary B2B social platform for most industries.
Twitter/X Engagement: Participate in real-time discussions, share insights, and connect with industry influencers. Twitter facilitates rapid information sharing and community building.
Industry Communities: Engage in forums, Slack channels, Facebook groups, and Reddit communities where your audience congregates. Provide value through helpful responses and insights rather than promotion.
Content Distribution: Share blog posts, research, and resources across social channels to expand reach. Optimize content format and messaging for each platform’s unique characteristics.
Employee Advocacy: Enable team members to share company content and insights with their networks. Employee voices often reach audiences brand channels cannot.
5. Content Marketing for Demand Generation
Content Strategy and Planning
Effective content marketing requires strategic planning aligned with business objectives:
Content Audit: Assess existing content assets, identifying gaps, opportunities, and performance trends. Understand what resonates with audiences and where coverage is lacking.
Topic Clusters: Organize content around core themes with comprehensive pillar pages supported by related cluster content. This structure improves SEO and user experience while demonstrating expertise.
Editorial Calendar: Plan content production and publication across channels, balancing evergreen resources with timely pieces. Maintain consistency while remaining flexible for emerging opportunities.
Content Formats: Diversify formats to match audience preferences and content goals. Include blog posts, whitepapers, ebooks, infographics, videos, podcasts, templates, and interactive tools.
Distribution Strategy: Plan how each asset will reach target audiences through owned, earned, and paid channels. Distribution often matters more than creation for content success.
Creating High-Converting Content
Quality content attracts, engages, and converts ideal customers:
Problem-Focused Approach: Address specific challenges your audience faces with actionable solutions. Content that solves real problems builds trust and positions your solution as valuable.
Data and Research: Support claims with statistics, case studies, and original research. Evidence-based content establishes authority and credibility that promotional messaging cannot.
Compelling Storytelling: Weave narratives that make concepts memorable and emotionally resonant. Stories about customer success, innovation journeys, or industry evolution engage readers deeply.
Actionable Takeaways: Provide specific steps readers can implement immediately. Practical value differentiates educational content from generic information.
Visual Design: Enhance readability through formatting, images, charts, and whitespace. Visual elements make content more scannable and engaging across devices.
Content Distribution and Promotion
Creating exceptional content is only half the equation:
Owned Channels: Publish on your website, email subscribers, social profiles, and other properties you control. Owned channels provide foundation for all distribution.
Earned Media: Pitch content to industry publications, contribute guest posts, and secure media coverage. Earned placements extend reach and build credibility through third-party validation.
Paid Promotion: Amplify top-performing content through targeted advertising, content syndication, and sponsored placements. Paid distribution accelerates awareness and lead generation.
Influencer Partnerships: Collaborate with industry influencers to co-create content or secure amplification. Influencer audiences trust their recommendations more than brand messages.
Repurposing Strategy: Transform core content into multiple formats for different channels. A comprehensive guide becomes blog posts, social content, video scripts, infographics, and email series.
Content Optimization and Iteration
Continuous improvement maximizes content ROI:
Performance Analysis: Track metrics including traffic, engagement, conversions, and pipeline influence. Identify patterns in high-performing versus underperforming content.
A/B Testing: Experiment with headlines, formats, calls-to-action, and distribution approaches. Systematic testing reveals what resonates most effectively.
Content Updates: Refresh existing assets with new information, improved formatting, and updated optimization. Updating content often delivers better ROI than creating new pieces.
User Feedback: Solicit input through comments, surveys, and conversations. Direct feedback uncovers content gaps and improvement opportunities.
Competitive Analysis: Monitor competitor content strategies, identifying strengths to emulate and weaknesses to exploit. Understanding the landscape prevents playing catch-up.
6. Account-Based Marketing (ABM) Integration
ABM Program Design
Account-based marketing represents the most targeted demand generation approach:
ABM Tiers: Structure programs with different engagement levels:
- Tier 1 (Strategic ABM): Highly personalized campaigns for 5-10 highest-value accounts
- Tier 2 (ABM Lite): Customized campaigns for 50-100 target accounts with shared characteristics
- Tier 3 (Programmatic ABM): Scalable tactics for hundreds of ideal fit accounts
Technology Requirements: Implement tools for account identification, engagement tracking, advertising, personalization, and measurement. ABM platforms integrate with CRM and marketing automation systems.
Team Structure: Assign dedicated resources to strategic accounts while maintaining shared resources for broader programs. Clear ownership ensures accountability.
Sales-Marketing Alignment: Establish shared goals, communication cadence, and collaboration processes. ABM fails without tight coordination between teams.
Target Account Strategy
Strategic account selection determines ABM success:
Ideal Customer Profile Fit: Prioritize accounts matching firmographic, behavioral, and needs-based criteria. Perfect fit accounts convert efficiently and deliver strong lifetime value.
Revenue Opportunity: Assess potential contract value, expansion possibilities, and strategic importance. Focus resources where returns justify investment.
Propensity to Buy: Consider timing signals including growth funding, leadership changes, technology migrations, and competitive vulnerabilities. Strike when accounts are most receptive.
Relationship Status: Factor in existing relationships, past interactions, and competitive positioning. Different approaches suit different relationship stages.
Personalized Campaign Execution
ABM campaigns demand relevance and customization:
Account Intelligence: Research business priorities, recent news, leadership team, technology stack, competitors, and industry challenges. Deep understanding enables meaningful personalization.
Custom Content Creation: Develop account-specific assets including personalized landing pages, custom presentations, industry-specific case studies, and executive briefings.
Multi-Touch Campaigns: Orchestrate touchpoints across email, advertising, direct mail, social media, and sales outreach. Consistent presence across channels reinforces messaging.
Executive Engagement: Facilitate connections between your leadership and account stakeholders through executive briefings, advisory boards, or co-creation opportunities.
Intent Signal Response: Monitor and respond to buying signals including website visits, content downloads, search behavior, and third-party intent data.
ABM Measurement
Demonstrate ABM impact through clear metrics:
Account Engagement: Track account-level activity including website visits, content consumption, ad impressions, email opens, and event attendance. Rising engagement indicates growing interest.
Coverage and Penetration: Measure progress reaching multiple stakeholders within accounts. Deeper penetration improves win rates and deal velocity.
Pipeline Metrics: Monitor opportunities created, deal velocity, win rates, and average contract value from target accounts. Compare performance against non-ABM accounts.
Revenue Attribution: Calculate revenue influenced by ABM programs, considering both sourced opportunities and acceleration of existing deals. Demonstrate clear ROI.
Relationship Strength: Assess stakeholder relationships, decision-maker access, competitive position, and overall account health. Strong relationships predict future revenue.
7. Technology Stack and Tools
Marketing Automation Platforms
Marketing automation orchestrates demand generation at scale:
Platform Selection: Choose solutions aligned with complexity, integration requirements, and growth trajectory. Leading options include HubSpot, Marketo, Pardot, and Eloqua.
Core Capabilities: Lead scoring, email marketing, landing page creation, form management, workflow automation, CRM integration, and reporting. Robust platforms handle full demand generation needs.
Implementation Best Practices: Start with foundational workflows before adding complexity. Ensure clean data, clear processes, and team training for successful adoption.
Segmentation Strategy: Organize contacts by firmographic attributes, behavioral signals, engagement history, and funnel stage. Precise segmentation enables relevant communication.
Lead Scoring Models: Develop scoring frameworks combining demographic fit with behavioral indicators. Effective scoring identifies sales-ready prospects while filtering noise.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM systems provide the foundation for demand generation data:
Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics: Leading platforms offer robust functionality with varying complexity and cost structures. Selection depends on sales process, team size, and integration needs.
Data Quality: Maintain clean, complete, standardized records. Data quality determines insight reliability and campaign effectiveness.
Pipeline Visibility: Configure stages, fields, and reports providing transparency into opportunity progression. Visibility enables accurate forecasting and bottleneck identification.
Marketing-Sales Integration: Ensure seamless data flow between marketing automation and CRM systems. Integration eliminates manual work and maintains single source of truth.
Analytics and Attribution
Measurement tools prove demand generation impact:
Google Analytics: Track website traffic, user behavior, conversion paths, and campaign performance. Enhanced ecommerce and goal tracking provide detailed insights.
Attribution Platforms: Solutions like Bizible, DreamData, or HockeyStack connect marketing activities to revenue outcomes through multi-touch attribution modeling.
Business Intelligence Tools: Tableau, Looker, or Power BI create comprehensive dashboards combining data from multiple sources for holistic performance views.
Call Tracking: Understand which campaigns drive phone inquiries through dynamic number insertion and conversation analytics.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Effective content delivery requires robust CMS capabilities:
WordPress, HubSpot CMS, Webflow: Popular platforms balance flexibility, ease of use, and functionality. Selection depends on technical capabilities and customization needs.
SEO Optimization: Ensure CMS supports technical SEO requirements including fast loading, mobile responsiveness, schema markup, and clean URLs.
Personalization: Advanced platforms enable dynamic content serving based on visitor attributes, behavior, and funnel stage.
Integration: Choose systems integrating seamlessly with marketing automation, CRM, and analytics tools.
ABM and Intent Data Platforms
Specialized tools enhance account-based strategies:
ABM Platforms: 6sense, Demandbase, Terminus, and Rollworks provide account identification, advertising, personalization, and measurement capabilities.
Intent Data Providers: Bombora, TechTarget, and ZoomInfo reveal which accounts research topics related to your solutions, enabling timely outreach.
Sales Intelligence: Tools like LinkedIn Sales Navigator, Clearbit, and Cognism provide detailed account and contact information supporting personalization.
Social Media Management
Coordinate social presence efficiently:
Hootsuite, Sprout Social, Buffer: Schedule posts, monitor mentions, analyze performance, and manage multiple profiles from unified dashboards.
LinkedIn Campaign Manager: Create and manage LinkedIn advertising campaigns with precise professional targeting.
Social Listening: Monitor brand mentions, competitor activity, and industry conversations to inform content and engagement strategies.
8. Measuring Demand Generation Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Track metrics aligned with business objectives:
Traffic Metrics: Website visits, unique visitors, page views, traffic sources, and new versus returning visitors. Traffic indicates awareness and interest levels.
Engagement Metrics: Time on site, pages per session, content downloads, video views, email engagement, and social interactions. Engagement signals message resonance.
Lead Metrics: Total leads, marketing qualified leads (MQLs), sales qualified leads (SQLs), lead source distribution, and lead quality scores. Lead volume and quality directly impact pipeline.
Pipeline Metrics: Opportunities created, pipeline value, pipeline velocity, conversion rates by stage, and deal size. Pipeline metrics connect marketing to revenue.
Revenue Metrics: Marketing-sourced revenue, marketing-influenced revenue, customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), and return on investment (ROI). Revenue metrics demonstrate business impact.
Account Metrics: Target account engagement, account coverage, penetration rate, and opportunity win rates by account type. Account metrics assess ABM effectiveness.
Attribution Modeling
Understanding which activities drive results enables optimization:
First-Touch Attribution: Credits initial touchpoint with conversion. Highlights what generates awareness but ignores nurturing impact.
Last-Touch Attribution: Assigns full credit to final interaction before conversion. Simple to implement but overlooks earlier influence.
Multi-Touch Attribution: Distributes credit across multiple touchpoints in the buyer journey. Options include linear (equal credit), U-shaped (emphasis on first and last), W-shaped (emphasis on first, middle, last), or time-decay models.
Custom Attribution: Develop models reflecting your specific sales process and stakeholder involvement patterns. Custom models most accurately represent reality.
Choose attribution approaches balancing sophistication with practical utility. Perfect attribution remains impossible, but directional insights enable better decisions.
ROI Calculation
Demonstrate financial impact through clear ROI analysis:
Investment Tracking: Capture all demand generation costs including team salaries, technology subscriptions, advertising spend, content creation, and agency fees.
Revenue Attribution: Calculate revenue influenced by demand generation through attribution modeling, considering both directly sourced and accelerated deals.
ROI Formula: (Revenue – Investment) / Investment = ROI percentage. For example, $500,000 investment generating $2,000,000 in revenue produces 300% ROI.
Payback Period: Determine how long demand generation investments take to return value. Shorter payback periods indicate efficiency.
Benchmark Comparisons: Evaluate performance against industry standards, historical results, and competitor intelligence. Context reveals whether results represent success.
Reporting and Dashboards
Communicate performance clearly to stakeholders:
Executive Dashboard: High-level metrics including pipeline, revenue, ROI, and key initiative status. Updated monthly for leadership review.
Operational Dashboard: Detailed metrics by channel, campaign, and tactic. Updated weekly or daily for demand generation team monitoring.
Campaign Reports: Comprehensive analysis of specific initiatives including performance, learnings, and recommendations. Created post-campaign for documentation.
Board Reports: Quarterly summaries connecting demand generation to business objectives, competitive position, and strategic priorities.
9. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Lack of Clear Strategy
The Problem: Many companies execute tactics without coherent strategy, resulting in fragmented efforts and inconsistent results. Activities don’t build on each other or advance toward clear objectives.
The Solution: Develop comprehensive demand generation strategy documenting target audiences, value propositions, channel priorities, content themes, and success metrics. Ensure team alignment on strategic direction before launching major initiatives.
Poor Sales-Marketing Alignment
The Problem: Marketing generates leads sales considers unqualified while sales complains about insufficient volume. Disconnection wastes resources and creates friction.
The Solution: Establish service level agreements defining lead criteria, handoff processes, and responsibilities. Schedule regular meetings between teams to review performance, provide feedback, and align on priorities. Create shared goals incentivizing collaboration.
Inadequate Lead Nurturing
The Problem: Companies focus exclusively on lead generation without nurturing prospects over extended buying cycles. Leads go cold before sales engagement or receive excessive, irrelevant outreach.
The Solution: Develop sophisticated nurture campaigns segmented by buyer stage, interests, and behavior. Provide valuable content addressing specific needs rather than generic promotional messages. Monitor engagement and adjust cadence appropriately.
Neglecting Existing Customers
The Problem: Demand generation focuses entirely on new customer acquisition while ignoring expansion opportunities within current accounts.
The Solution: Extend demand generation principles to customer marketing with content supporting adoption, upsells, cross-sells, and advocacy. Customer expansion typically converts more efficiently than new acquisition.
Measurement Limitations
The Problem: Companies track vanity metrics without connecting activities to revenue outcomes. Inability to prove ROI undermines budget justification and strategic decisions.
The Solution: Implement attribution modeling connecting touchpoints to pipeline and revenue. Establish clear KPIs aligned with business objectives. Invest in analytics infrastructure providing accurate, actionable insights.
Over-Dependence on Single Channels
The Problem: Companies concentrate efforts on one channel like paid search or content marketing, creating vulnerability to algorithm changes, competitive pressure, or market shifts.
The Solution: Diversify across multiple channels balancing quick wins with sustainable long-term approaches. Maintain testing budget for exploring emerging opportunities.
Insufficient Testing and Optimization
The Problem: Teams execute campaigns without systematic testing or learning from results. Performance plateaus as markets evolve and competition intensifies.
The Solution: Build experimentation into processes with dedicated budget and clear testing frameworks. Document learnings and apply insights to future initiatives. Establish culture valuing data-driven iteration.
10. Future Trends in B2B Demand Generation
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI technologies transform demand generation execution:
Predictive Lead Scoring: Machine learning models analyze patterns predicting which prospects will convert, enabling more intelligent prioritization than rule-based scoring.
Content Personalization: AI enables dynamic content serving based on visitor attributes, behavior, and predicted interests without manual segmentation.
Chatbot Enhancement: Natural language processing improves bot conversations, qualifying leads and answering questions effectively before human involvement.
Campaign Optimization: AI algorithms automatically adjust bidding, targeting, creative, and timing to maximize performance across paid channels.
First-Party Data Strategies
Privacy regulations and cookie deprecation require new approaches:
Zero-Party Data Collection: Directly ask prospects about preferences, challenges, and interests through progressive profiling and preference centers.
Customer Data Platforms: Unify data from all touchpoints creating comprehensive profiles while respecting privacy boundaries.
Value Exchange Models: Provide sufficient value in exchange for information, moving beyond gated content toward meaningful relationship building.
Video and Interactive Content
Content formats evolve toward higher engagement:
Short-Form Video: Platforms like LinkedIn and Instagram emphasize video content. B2B brands adapt with educational shorts, thought leadership clips, and quick tips.
Interactive Experiences: Calculators, assessments, configurators, and interactive infographics provide personalized value while capturing engagement data.
Live Streaming: Real-time content including Q&A sessions, product launches, and behind-the-scenes glimpses builds authentic connections.
Community-Led Growth
Communities become demand generation engines:
Peer Communities: Forums, Slack channels, and membership platforms where customers and prospects connect independently of transactions.
User-Generated Content: Customers create content showcasing use cases, results, and innovations, providing authentic social proof.
Collaborative Learning: Educational programs bringing customers together to develop skills and share best practices while building brand loyalty.

Leave a Reply